From Rii
m |
m |
||
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
Some design examples are as fellows. | Some design examples are as fellows. | ||
{|border="1" align="center" cellpadding="5" | {|border="1" align="center" cellpadding="5" | ||
| - | |align="center"|Pole-knocking Machine Design Example 1 | + | |align="center"|'''Pole-knocking Machine Design Example 1''' |
| - | |align="center"|Pole-knocking Machine Design Example 2 | + | |align="center"|'''Pole-knocking Machine Design Example 2''' |
|- | |- | ||
|[[Image: VM350_project3.gif]] | |[[Image: VM350_project3.gif]] | ||
|[[Image: VM350_project4.gif]] | |[[Image: VM350_project4.gif]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| - | |align="center"|Walking Machine Design Example 1 | + | |align="center"|'''Walking Machine Design Example 1''' |
| - | |align="center"|Walking Machine Design Example 2 | + | |align="center"|'''Walking Machine Design Example 2''' |
|- | |- | ||
|[[Image: VM350_project5.gif]] | |[[Image: VM350_project5.gif]] | ||
|[[Image: VM350_project6.gif]] | |[[Image: VM350_project6.gif]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| - | |align="center"|Kitchen Cabinet Design Example 1 | + | |align="center"|'''Kitchen Cabinet Design Example 1''' |
| - | |align="center"|Kitchen Cabinet Design Example 2 | + | |align="center"|'''Kitchen Cabinet Design Example 2''' |
|- | |- | ||
|[[Image: VM350_project1.gif]] | |[[Image: VM350_project1.gif]] | ||
|[[Image: VM350_project2.gif]] | |[[Image: VM350_project2.gif]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
Latest revision as of 09:15, 9 October 2014
Design and Manufacturing II
Course Description
The goal of this course is to give students an understanding of the basic engineering principles behind common mechanical systems, as well as how to utilize their engineering knowledge to both synthesize and analyze their own simple mechanical systems and components. At the end of this course, students should be able to do the following, in either a team setting or individually:
- Design (synthesize) basic mechanical systems (including components such as linkages, cams, bearings, and gears) and mechatronics systems (which integrate electronic control and mechanical components) to satisfy given motion requirements.
- Perform analyses of the underlying kinematics of a mechanical system to predict behavior and evaluate key mechanical quantities (trajectory, velocity, acceleration, force, etc).
- Apply appropriate selection criteria to choose standard mechanical components such as gears, bearings and springs.
- Virtual prototyping of mechanical systems using one or more commercial CAD programs (IDEAS, Unigraphics, ProEngineer or AutoCAD) for performance and/or strength check
- Test and evaluate the physical prototype of simple machine systems and components for performance and benchmarks
- Critique and redesign mechanical systems and components for enhanced performance and reliability.
Prerequisites
VM250 is the only official prerequisite. You are expected to have: i) a basic working knowledge of elementary mechanics (statics, dynamics, and strength of materials), ii) basic machine shop skills and training on core shop machinery (mill, drill, bandsaw, lathe, laser cutter, etc).
Machine Shop Training
If lathe or mill will be used to fabricate project designs, a machine shop training should be finished by the student operator. To work on the projects properly, the operator should know the basics of setting proper feed rates and speeds, as well as how to choose the correct tool for a given application. What’s more, students all should practice good shop safety habits, such as proper clothing and safety glasses. Besides the lathe and mill, rapid prototyping machine and laser cutter can also be used for the projects. Specific safety rules should also be strictly followed.
It is important to remember that the machine shop is a shared resource among VM250, VM350, and VM450. Students from VM450 might have higher priorities to access the shop.
Textbook
There are three textbooks used for references in VM350, some chapters are available in protected PDF format:
- Richard Budynas and Keith Nisbett, Shigley’s Mechanical Engineering Design, 8th Ed., McGraw-Hill, 2007
- Robert L. Norton, Design of Machinery, 4th Ed., McGraw-Hill, 2008
- A. G. Erdman, G. N. Sandor, and S. Kota, Mechanism Design: Analysis and Synthesis, 4th ed. vol. I: Prentice Hall, 2001
Course Components
There will be homework assignments, a closed-book in-class midterm, a closed-book in-class final exam and group projects.
Sample projects are as follows. Students will work in four-person teams on these projects.
- An electronics project where students will learn how to implement a closed-loop control system
- This short project will serve as an introduction to the design and implementation of electronic control systems. Students will gain hands-on experiences in using a microchip controller, connecting electronic circuits and writing programs.
- Goal of this project is to use a controller to control a R/C servo motor to swing a serially connected chain quickly as high as possible.
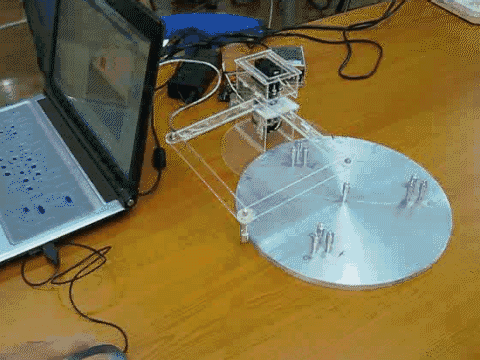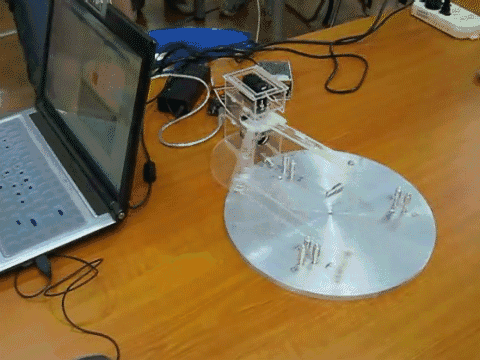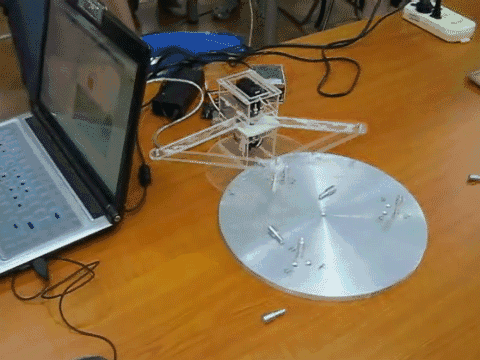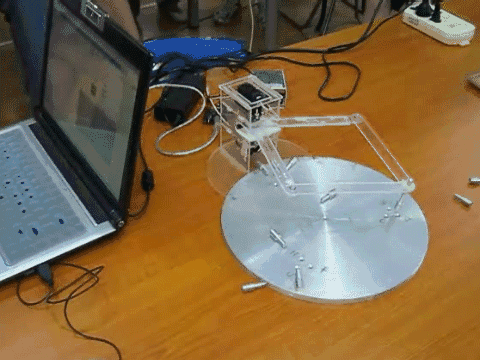
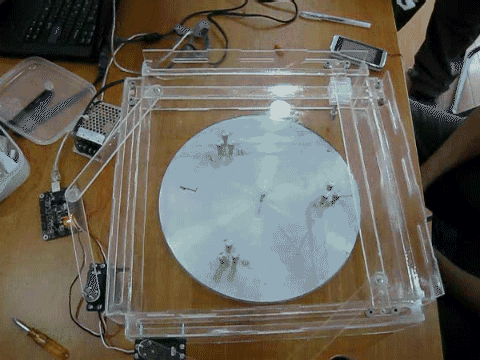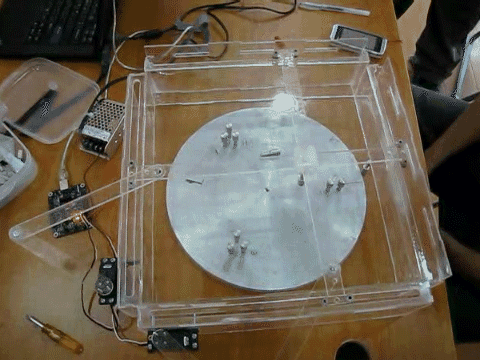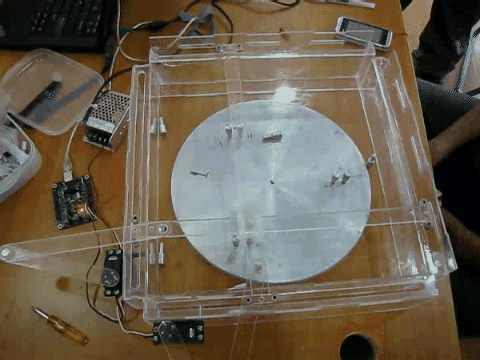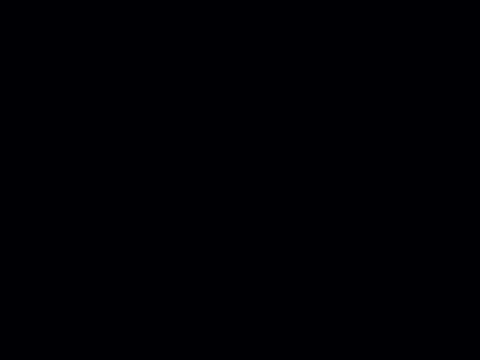
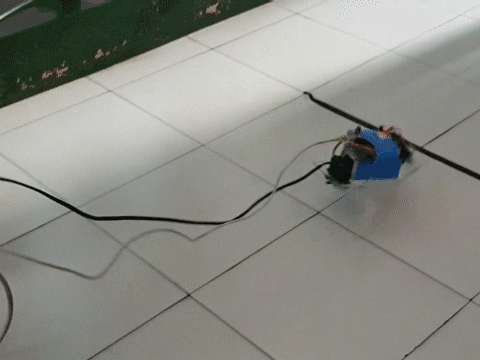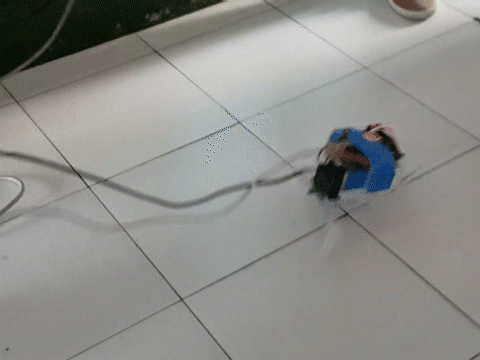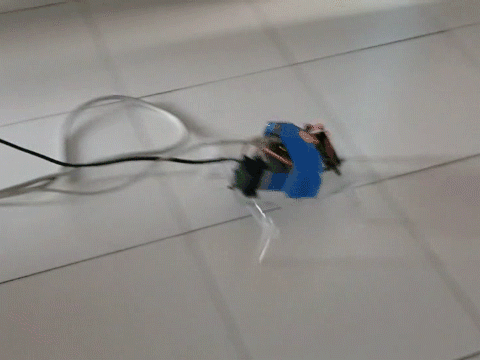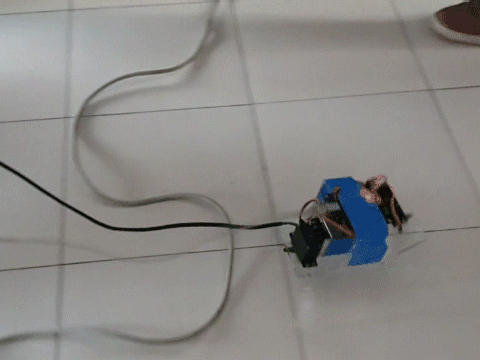
- A mechatronics project where students design and construct a pole-knocking machine
- Goal of this project is to design and construct a planar mechanism which holds a pole to knock down other poles in a specified sequence.
- The mechanism will be driven by two R/C servo motors, and the motors’ motions will be controlled by the implemented control system.
- Once set up, the only control is to push a start button to set the system in motion.
- Knocking down all the poles in the desired sequence is one success.
- Teams would compete for the fastest success.
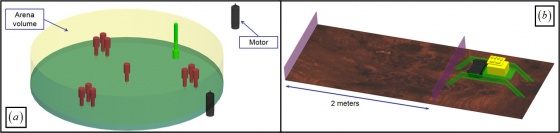
- A mechatronics project where students design and construct a walking machine
- Goal of this project is to design and construct a walking machine with on-board a controller and a power supply. Everything should be enveloped by a 200mm×200mm×200mm volume.
- The mechanism will be driven by two R/C servo motors, and the motors’ can only rotate for 180°.
- Once set up, the only control is to push a start button to set the system in motion.
- The competition is to finish the 2-meter walk as soon as possible.
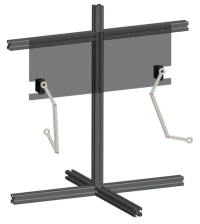
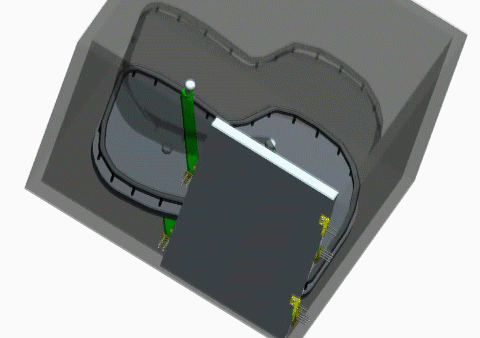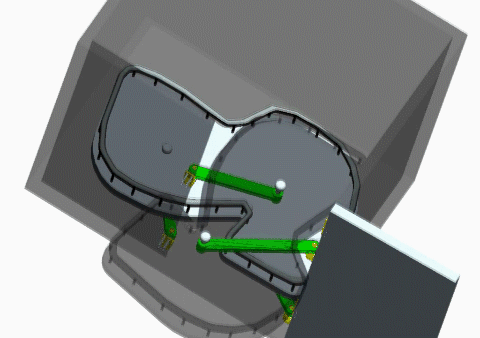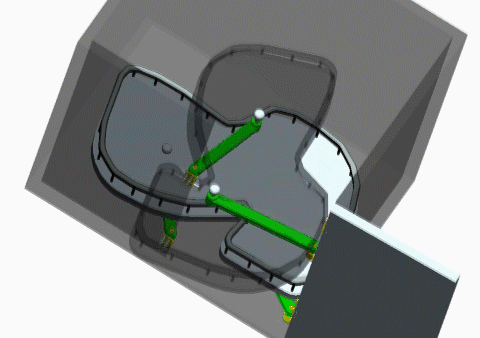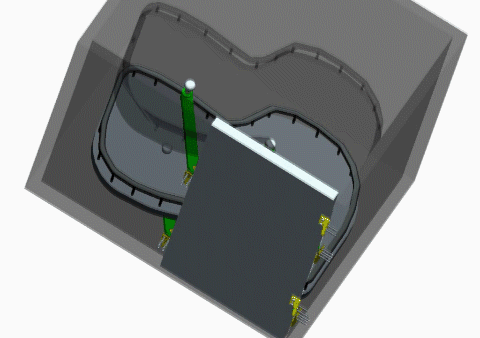
- A design project where students design a kitchen cabinet using a CAD software
- Goal of this project is to design a mechanism so that the space around the corners could be easily accessed.
- Everything should be enveloped by a 800mm×600mm×800mm volume.
- The use of standard parts (e.g., bearsings, screws, shafts, etc.) and customized parts should be properly balanced.
- An animation should be generated to show a complete motion cycle of the design
Some design examples are as fellows.